Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring
Surgery Overview
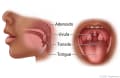
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are surgeries to remove the tonsils or adenoids. The adenoids are above the tonsils and behind the nose. Your doctor will do the surgery through your mouth. You will be asleep. Most people go home that same day.
These surgeries are:
- Used to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in children.
- Rarely used to treat snoring in adults.
- Not used to treat snoring in children.
What To Expect
You may need to be watched closely after surgery. Your care team will watch:
- Your blood oxygen levels.
- For throat swelling, nerve injury, and sleepiness. Both the surgery itself and the medicines used can cause this.
Your throat will be sore after surgery. You may find it hard to eat and swallow for a few days.
Children who are younger than 3 years and who have other conditions, such as Down syndrome, are more likely to have problems from surgery. The most common is having a hard time breathing. These children may need oxygen therapy or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy after surgery.
Why It Is Done
Your doctor may suggest these surgeries to treat sleep apnea if you have swollen tonsils and adenoids that block your airway during sleep. This surgery is often the first treatment choice for children. That's because swollen tonsils and adenoids are often the cause of a child's sleep apnea.
How Well It Works
In children with sleep apnea, symptoms may get better over time. Caregivers reported a decrease in things such as:footnote 1
- Snoring, coughing, and colds.
- Some behavior problems.
- Restless sleep.
Some children with sleep apnea who do not have the surgery also get better over time.
Risks
Possible risks after surgery include infection and a lot of bleeding. Some bleeding is expected.
References
Citations
- Venekamp RP, et al. (2015). Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical management for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews(10): CD011165. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011165.pub2. Accessed September 24, 2020.
Credits
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Venekamp RP, et al. (2015). Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical management for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews(10): CD011165. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011165.pub2. Accessed September 24, 2020.